As breast augmentation procedures have sky rocketed in popularity, patients coming to see plastic surgeons present with many different varieties of breast shapes, as well as different degrees of sagging and variable levels of breast atrophy and breast volume loss. Therefore, many different breast augmentation techniques have been developed for silicone breast implant placement to address the concerns patients might have about their breast shape and size. Despite this, patients are typically not aware of the different breast enhancement options which could include under the muscle breast implant placement with or without a dual plane, above the muscle breast augmentation but under the pectoral muscle fascia (subfascial), and above the muscle but under the breast gland only (above the fascia). We discuss the important differences below in order to improve our patient’s understanding of the steps involved with their breast augmentation procedure.
What are some of the under muscle breast implant techniques?
Under the muscle breast augmentation is the most popular method of performing breast enlargement surgery with either silicone breast implants or saline breast implants. The number one reason plastic surgeons choose to go under the pectoral muscle is because the results are better, especially in the long-term, and by going under the pectoral muscle the risks of capsule contracture are much lower when compared to most above the muscle breast augmentation procedures.
In addition to improving the overall softness of breast implant results by going under the pectoral muscle, the muscle itself acts to add more tissue over the breast implants making the breasts feel softer. The muscle itself can also act to support the extra weight of the breast implants, and perhaps lead to a decrease in the effects gravity might cause over time. Many patients with under the muscle breast implants sag less when compared to above the muscle breast enlargement surgery.
Can you still go under the muscle if you are a little saggy?
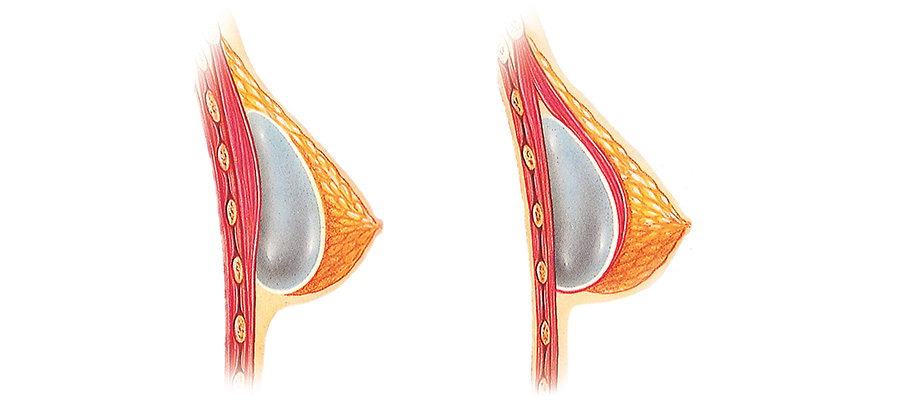
Sagging breasts are common and tend to occur after weight loss and pregnancy. Depending on the level of sagging, a plastic surgeon might consider either a breast lift surgery with breast implants or a breast augmentation with the option to go under the pectoral muscle using the dual plane technique or above the muscle surgery. The decision to choose one plastic surgery approach versus another depends on the patient’s goals and the level of sagging. For the cosmetic surgeon, the level of breast sagging will be the most critical factor in recommending one technique versus another.
The dual plane breast augmentation is the procedure recommended most often in patients that are just a little saggy. The level of sagging is typically determined using measurements of the breasts during a consultation. Oftentimes, a plastic surgeon uses the term “pseudosaggy breasts” to describe breasts which have some sagging characteristics, but can still be treated with breast augmentation. Moderate or severely sagging breasts are best treated with a breast lift technique in addition to breast implants.
Can you still go under the muscle if you exercise your upper body a lot?
Once a breast implant is placed under the pectoral muscle it will find itself under the influence of the muscle’s power to be moved around and shift when the muscle contracts. As the body’s second largest muscle, the pectoral muscles are very powerful. This is especially true if you work out a lot. Having a strong upper body, which is typically achieved with pullups and pushups, leads to the development of stronger and bulkier pectoral muscles. As a result, the ability of the pectoral muscle to move the breast implants around while you’re exercising or when you flex your muscles is increased. The movement of the breast implant under the muscle’s contractile power is predictable and results in an upward movement of the breast implant towards the clavicles. One way to mitigate this contractile movement is to limit the level of exercise in the upper body after breast augmentation. However, committed athletes are generally not willing to make this drastic lifestyle change.
A second option, which should be discussed with your breast surgeon, is performing the breast augmentation using a dual plane approach. In the dual plane approach, the breast specialist will release the pectoral muscle origin at the rib margin. This step will reduce the ability of the pectoral muscle to contract in such a way as to push the breast implant less powerfully, limiting breast implant show at the clavicle. The dual plane will reduce the strength of the pectoral muscle, so serious athletes typically find this option less than ideal. At this point, discussing an above the muscle breast augmentation to preserve the ability and strength of the pectoral muscles to contract while reducing the movement of the breast implants should be discussed with your plastic surgeon. If you enjoyed this blog on breast implant placement and would like to learn more, you should stay tuned for our upcoming blog which details the above the pectoral muscle breast augmentation procedures. Next time, we will discuss the above the muscle breast implant placement with the subfascial approach and the above the fascia approach.
If you’re interested in finding out which type of breast augmentation approach suits your anatomy best, or you are ready to discuss your future breast augmentation results, please call (480) 382-4995 to make an appointment with Guerra Plastic Surgery Center.


